It can be easy to remember the past Golden Era for BigLaw: Say, the decade preceding the 2008 Great Financial Meltdown. And you would not be wrong to recall it that way. No indulgence in nostalgia is required; that decade constituted an unheard-of run of economic strength for BigLaw.
You want proof? A few weeks ago, ALM Intelligence published the remarkable Jae Um’s Outwit, Outplay, Outlast: A Post-Recession View of the Survivors, which among other things included a sensational chart distilling the fiscal year performance of every AmLaw 50 firm for each of the past 20 years, 1998–2017. (Keep reading and you’ll come to it.)
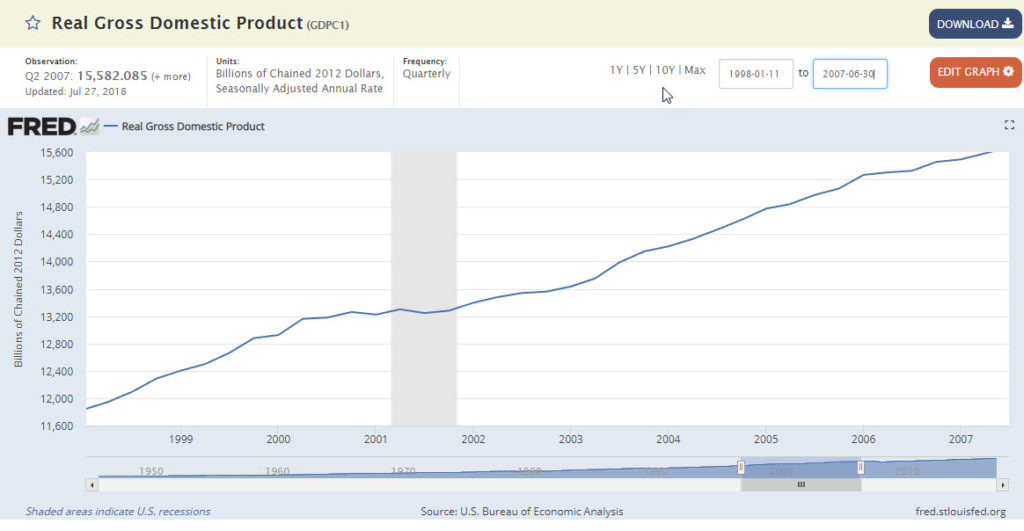
We’ll start with the Golden Era: the years 1998 through 2007.
Of the 500 fiscal years represented (50 firms x 10 years), care to guess how many down years (revenue shrinkage) there were?
I won’t torture you: Four, or 0.8%. Meanwhile, the number of fiscal years of purely flat, zero-growth revenue was five. Put these together and any randomly selected firm’s odds of growing revenue from one year to the next was 98.2%–for an entire decade. All you had to do was stand there, in that cohort, during that decade. Under capitalism, this is unheard-of.
The years from 2009 through 2017 have constituted a dramatic departure.
Technical note #1: I omit 2008 because some firms were still benefiting from collections and other lags held over from the palmy days but others were hit early, the severity and speed with which firms were “hit” varied tremendously and was essentially random (I was front-row witness to the last months of Thacher Proffitt, which went from demand for 300+ associates churning out securitizations to 0 in about 24 hours), and also because no one had much time to react to the new economic order. But if you’re asking, 10 firms were down and four were flat that year
Technical note #2: I do include 2009 as the first year of our second time span because it was, after all, a real year and emblematic of our new era.
During that second 9-year span:
- 43 of the 50 have experienced one or more down years;
- 6 of the remaining 7 had at least one flat year; and
- One and only firm has put together an unbroken streak of up years.
The technical term for this is “volatility.”
What changed? Let’s take a closer look at US economic performance during those two periods, shall we? Perhaps the economy is to blame. Hardly anyone has experienced the last decade as a period of rampant prosperity. On top of incessant client rate pressures, the escalating arms’ race for lateral talent, de-equitizations, and stringent cost control, what if we’ve simply all been facing macroeconomic headwinds?
So I decided to take a look. (Almost all the following data comes from the St. Louis Federal Reserve’s priceless “Fred, which one of the Times’ best business journalists calls “an economic writer’s best friend.”)
The obvious place to start is GDP growth over those two periods. Shall we?
It grew from $11.9 trillion to $15.6 trillion in “chained” dollars, or about 37.1%. (“Chained” dollar series embed a more sophisticated and accurate adjustment for inflation than constant dollar series. Constant series rely on a static basket of goods and services to define the inflation rate, whereas chained series tie dollar values to an updated, rolling or “chained” basket of what people are actually purchasing during each pertinent time period. Next time you have a choice between citing the same economic data in constant vs. chained form, go for chained.)
And real GDP from 2008 to 2018:
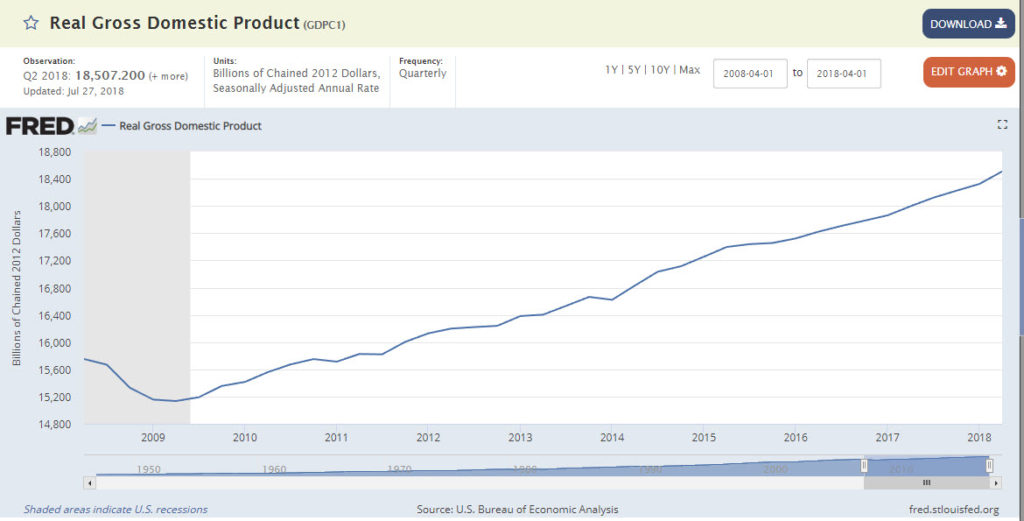
Fred Chained Dollar US GDP 2008-2018. It went from about $15.2 trillion at the trough to $18.6 trillion mostly recently. Up 22.4%, so no, not as strong as our chosen prior period, but no support for anyone hypothesizing that BigLaw’s problems are exogenous macroeconomic headwinds.
Let’s look at a few other statistics arguably more indicative, or more closely correlated, with demand for BigLaw’s services than pure GDP.



Bruce, this neatly addresses one of the two explanations of the “slow growth” issue discussed by Nicolas Bruch in his Feb 2018 article (n1), i.e. “broader economy” vs. “increased competition”.
Without getting into the nuances of those two theories, I think a third type of possible explanation is also worth throwing into the mix, to do with scalability.
Starting with the observation that, within a given firm, lawyer headcount is, of course, a key driver of revenue on the standard business model –
* What if such headcount is only scalable up to a certain point (high hundreds / low thousands?) before the resultant costs and constraints impede the ability to grow further while maintaining / enhancing profitability and stability?
* What if, also, for many large, highly profitable firms, that point had been more-or-less reached by 2007?
I don’t have access to the AmLaw dataset, but Legal Business did a striking analysis in Dec 2017 of large UK firm revenue growth in the last ten years compared with the ten years before. Quoting from the editor’s summary (n2):
“Stripping out shops that executed large-scale mergers, have been taken over or who entered or exited the top 100 during the ten years, left us with 53 firms for a roughly like-for-like comparison of underlying growth. The top firm is Mishcon de Reya, holding the spot after nearly quadrupling its income between 2007 and 2017. The rest of the top ten is comprised of largely mid-weight players, including Watson Farley & Williams (WFW), Fieldfisher, Osborne Clarke, Stephenson Harwood and Holman Fenwick Willan, with all of these firms comfortably doubling revenues. With the exception of Bird & Bird, none of this group generated even £100m at the height of the 2000s’ boom. Equally striking is that many of the top-tier legal brands rank in the lower reaches of the table. Allen & Overy (A&O) sits in a lowly 24th slot. Freshfields Bruckhaus Deringer, Clifford Chance and Linklaters, meanwhile, cluster in the bottom third of the table, coming after a 2016/17 when their revenues all got a sizeable forex-induced bump. Other major firms in the bottom quartile for revenue growth include Simmons & Simmons, Eversheds Sutherland and Addleshaw Goddard. So much for the notion of the big law firms pulling away or a flight to quality.”
Of course it would be foolish to suggest a single cause for anything this complex, but my impression is that the impact of organisational size has been non-trivial in the last ten years, and I suspect there are various factors which will make it more significant over the next ten.
(1) https://www.law.com/2018/02/14/why-are-law-firm-growing-so-slowly-the-answer-may-/
(2) https://www.legalbusiness.co.uk/comment/super-growth-or-decline-which-firm-are-you/
Graeme:
Fascinating on all counts. A couple of supplementary thoughts:
I’ve spent a fair amount of time wondering where those pre-2008 good ol’ days went and whether they may return. My perspective is primarily the litigation side of the business. Here are a few thoughts:
1) Pricing pressure – clients started questioning bills. A case that pre 2008 would have fetched $5 million post 2008 was worth $1.5-2M. They hired cadres of in house lawyers to review and cut bills, negotiate fee caps and flat fees, and force firms to do in depth, free “pitches” for cases. They convinced firms to take cases as a “loss leader” but never followed up with more work because there is a never ending supply of new firms. They eliminated block billing, team meetings, and document review by associates. All of that reduced firm revenue and is unlikely to go back to the way it was.
2) Specialization – someone, be it firms or clients, decided highly specialized lawyers were a better sell. Now rather than having litigators, you have commercial and patent and soft IP and antitrust and class action and bankruptcy. If one area has a down year you have extra capacity because it is too hard to move a specialized lawyer to another area.
3) Streamlined cases – the pricing pressures combined with doc review by people who don’t know the case means there are fewer depositions, less motion practice, and fewer trials. This also means there are far fewer opportunities for young lawyers. As a second year associate at a big NY firm, I took depositions. Years later when I was at a big Chicago firm, associates were making partner having only ever taken one deposition in their 7th year.
Ultimately I don’t see how it can ever go back to what it was. But I also don’t think the old guard in firms has truly adapted. Rather the focus is on lateral hiring and increased hours from fewer associates. It’s not sustainable.
Dear Allison:
First of all, thanks for your truly reflective response, providing perspective from someone who was there “before” and “after.”
While I heartily agree with all three of your primary observations, permit me to add a few supplementary thoughts starting from your closing observation that “the old guard in firms has[n’t] truly adapted” and that the focus on lateral hiring (a zero-sum game) and flogging the associates’ hours harder (all kinds of malign consequences from low morale to time-padding temptations to hoarding, and on and on) are neither sustainable nor smart ways to run a business.
I see a common thread in all three obstacles you point out: If we continue to refuse to “truly adapt,” they’re essentially insoluble. They are evolved features of the system we have built and that clients have learned now (to our rue) to adapt more to their purposes. We can’t claim (see much of the above) that clients are doing anything we didn’t open the door to their doing, and invited them to walk through on top of that. (If we didn’t raise rates every year, maybe discounts would erode and realization would improve.)
The answer as I see it has to start with a combination of more flat-fee and project/staged billing. While we’re at it, we have to take the lateral recruitment needle out of our arms. Hire very very selectively to fill gaps in capability, yes; try to rent revenue with stupendous friction and transactional costs upfront, no.
Finally, where will all the veteran, experienced sages of the future come from if there’s nowhere for them to be trained because there’s nothing for them to do (NewLaw + AI have stepped in) as juniors? I have no snappy answer to this. But I’m working on it.
Thanks again.
A note on the much-maligned concept of “command and control” as a management style. The archetype of command-and-control management is the military, where the full formulation is usually command-control- communications- and-Intelligence, “C^3” (c-cubed). The additional terms – especially translated at least partly metaphorically, to business – matter. A command-control management without communications would be the sort of straightjacket that many fear, and unless the system is underlain by appropriate “intelligence” (which today, of course, may be AI, at least in part) we know that the probabilities of success diminish, often rapidly, toward zero. It would be interesting to see how people familiar with operating C^3 in high-stakes businesses (even as “counselors”, for example at McKinsey) would see its appropriate application to Law.